VPN technology is a quick emergency exit when the regimes block the sites that criticize them, and using this technology we can enter the Internet through a free port, but can we trust the source of this port? And what are the risks?
An increasing number of countries are blocking undesirable websites on their national networks, and are searching the Internet specifically for critical and opposing voices.
 |
| Virtual Private Networks |
When the Internet becomes a state-controlled intranet, users run into the problem that they are no longer able to visit some sites, such as Deutsche Welle for example, and other free media sources. The social media platforms, which opposition activists used to protest through, are also no longer available online.
Quick fix: VPN
When a ruling regime imposes censorship on the Internet during a crisis, many users turn to the simpler solutions, often in the form of VPN technology.
This technology was developed to allow companies located in different places to connect their internal networks, known as the Intranet, via encrypted channels found on the regular Internet. However, VPNs can also be used to connect private computers, connected to a government-controlled Internet, with another service provider that provides Internet without government control..
VPNs abound, and service providers make great promises. They say that when you install the software needed to run on your phone, you'll be able to access the Internet safely. The service providers also promise to protect your personal data from access by any potentially harmful parties .
What is clear is that by using VPNs you can use the Internet, via service providers in other countries, bypass government censorship and access blocked websites.
How does this technique work?
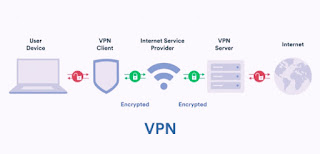
A VPN creates an encrypted tunnel that connects your mobile phone or computer to a remote service provider, and through that service provider you can access the Internet.
And when you start searching the web, it appears to the operators of the websites you visit as if your device itself is a VPN service provider.
For example, if you are using a computer or mobile phone in Germany while the VPN service provider is located in Japan, the operators of the sites you visit will think that you are in Japan and not in Germany. This invisibility game is based on the idea that you do not appear online with your device address, but with the address of your VPN service provider.
 |
| Infographic VPN |
Can the user's identity be revealed and accessed?
Virtual private networks areVPN is now available to everyone, and the software required to run it is also available for free. However, users often avoid thinking about the risks a situation might involve.
Systems that control the Internet in general can detect that a person is using VPN technology. But they cannot reveal what this person is doing and the nature of the data they sent and received through the encrypted tunnel.
For this reason, some dictatorial regimes have decided to prevent the use of this technology, either by blocking access to service providers located abroad, or sometimes, in rare cases, by prosecuting those who use it..
But governments of countries usually cannot take any action against all virtual private networks, as many foreign companies in these countries rely on this technology to secure each company's internal communications network. As long as the government does not block the addresses of VPN service providers, they can then be used to bypass state-imposed censorship.
How secure is personal data?
Here lies the second weakness, which is the access of all your data to the party or company that provides you with the VPN service. But how well do you know that company, as you have to trust that the service provider will protect the privacy of your data.
Because your service provider operates the encrypted tunnel, it also has the ability to know what sites you visit and when and how often you use them. It also has the ability to view the unencrypted content of all your communications, such as your email.
This data can be saved and sold for commercial purposes, especially data related to your internet searches, which could turn into a successful business model for VPN service providers. They can also get money from customers using a subscription system, and then sell users' data about their internet usage behavior to advertising agencies.
In the worst case, they can also sell or supply your data to government agencies. Even if the service provider promises not to sell your data, there will be a permanent risk to this data simply because it is stored with them. Not a single day passes without reporting a data leak, whether due to poor security or a criminal attack by hackers.
What is the best solution?
The best way is to never collect and save data, even if the VPN provider promises not to keep your data. A system that does not collect any data is more secure, which is what a program and an Internet browser canTor done.
The program builds a triple tunnel directly towards the Internet browser, where it provides the user with levels such as the onion layers, named after them, so that none of these layers knows your identity and your destination. By using this program it is not possible to store the pages and sites that you visit and the extent of your use of them, as this data is not available to it at all. That is why this program and the way it works are called “Privacy by Design”.
consideredTor is a not-for-profit project that is run by volunteers and can be used for free. But there is one drawback, as sometimes connecting to the Internet can be difficult, so speed and ease become a high price for the privacy you get..
 |
| TOR |
And if you want to browse the Internet quickly using your regular browser via a foreign address, without the need for the greatest degree of protection for your data, you should use a VPN service providerA VPN you can trust as much as possible.
That is why it is better not to rely on portals that compare providers of this technology and classify the services they provide, as these portals often provide recommendations for financing or sponsoring the service providers themselves. The alternative is to ask trusted digital security professionals, or check out the latest reviews of VPNs published in reputable specialist sources..
What are the effects we leave behind when using the Internet?
When computers connect to each other on the Internet, a permanent exchange of hardware addresses occursIP address.
But this does not necessarily mean that people are identified because those email addresses are rarely tied strictly to the people using the devices.
The same applies to data files known as cookies. If the user closes them, their role stops or their importance ceases . Google recently announced that it does not want to continue using cookies, which collect data for third parties, through the company's Google Chrome browser...
What is more, today's Internet users can be identified more specifically by what is known as fingerprinting. What is meant is that the browser collects relevant information about the user, such as the area in which he is located or his devices connected to the Internet, which enables the user to be identified with an accuracy that can reach 99 percent through these electronic fingerprints..
This method is very popular with the major Internet companies. For example, entering your account on a site such as Amazon or Google means linking the electronic fingerprint to a specific real person.
Sometimes these fingerprints are not collected directly on the websites of these giant companies, as a third party also collects them. For example, if you visit a website that contains images saved or found on a third-party service provider or website, that third party can also access you..
Add Comments